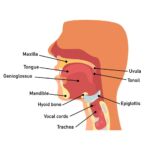
The throat, also known as the pharynx, is a muscular tube that runs from the back of the nose down into the neck. It’s a passageway for air, food, and liquid, and also helps with speech. The throat contains many structures, including:
Nasopharynx: The top of the throat, connecting the nose to the respiratory system. It contains the adenoids and tubal tonsils, which are part of the immune system.
Oropharynx: The middle of the throat, containing the tonsils at the base of the tongue. Air, food, and fluid pass through the oropharynx.
Hypopharynx: The bottom of the throat, regulating how food moves to the esophagus and air moves to the lungs.
Larynx: Also known as the voice box, the larynx is protected by the epiglottis, which keeps food and liquid from entering the respiratory system.
Epiglottis: Protects the larynx and the ability to breathe.
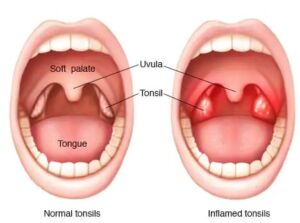
Tonsils: Located in the oropharynx.
Tonsillectomy
A tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the tonsils. Tonsils are two small glands located in the back of your throat. Tonsils house white blood cells to help you fight infection, but sometimes the tonsils themselves become infected.
Tonsillitis is an infection of the tonsils that can make your tonsils swell and give you a sore throat. Frequent episodes of tonsillitis might be a reason you need to have a tonsillectomy. Other symptoms of tonsillitis include fever, trouble swallowing, and swollen glands around your neck. Your doctor may notice that your throat is red and your tonsils are covered in a whitish or yellow coating. Sometimes, the swelling can go away on its own. In other cases, antibiotics or a tonsillectomy might be necessary.
- Recurrent throat infections
If a child has at least seven infections a year, more than five infections a year for two years in a row, or three infections a year for three years
- Obstructive sleep apnea
If enlarged tonsils block the airway and cause a child to stop breathing during sleep
- Chronic throat infection
If an adult has had several sore throats over 1 to 3 years, or a sore throat and swollen tonsils for at least 3 months
- Cancer
Different methods for tonsils removal
- TONSILLECTOMY WITH R.F.
Radiofrequency (RF) tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to remove tonsil tissue
- TONSILLECTOMY WITH COBLATION
A coblation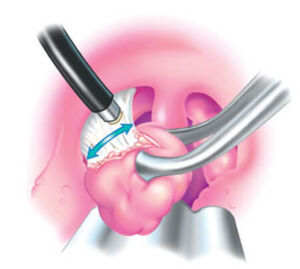 tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the
tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the
tonsils by destroying the tissues that attach them to the pharynx.
The procedure uses a coblation wand and a saline solution
to gently and precisely remove the tonsils.
Why Is Coblation Tonsillectomy A Better Choice?
Patients report a better overall experience with Coblation Tonsillectomy after surgery when compared to traditional procedures. Studies show that patient calls and visits to the doctor due to complications after surgery are significantly less with Coblation Tonsillectomy.1Because of tissue damage caused by the heat of traditional tonsillectomy procedures, patients often take up to two weeks to return to a normal diet and to resume normal activity. Coblation Tonsillectomy is the gentle alternative offering a rapid recovery and minimal pain, with most patients resuming a normal diet and activities within just a few days.
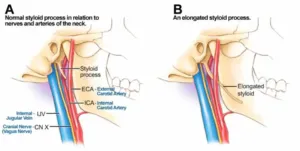
STYLOIDECTOMY
MICROLARYNGEAL SURGERY
Microlaryngeal surgery (MLS), also known as microlaryngoscopy or microscopic laryngeal surgery, is a minimally invasive procedure that allows a surgeon to view and operate on the larynx and vocal cords:
VOCAL CORD POLYPS:Vocal cord polyps are often the result of an acute injury and typically occur on only one vocal cord. Polyps may have several other causes, including gastroesophageal reflux, or chronic inhalation of irritants (such as cigarette smoke). Polyps tend to be larger and bulge out more than nodules. Polyps are common among adults.
VOCAL CORD NODULES: Vocal nodules are benign (non-cancerous) growths that can form on the vocal cords. They develop if you use your voice too much, and result in hoarseness and problems with your voice
VOCAL CORD LESIONS:
I am text block. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.